WHERE THE EXTRA MILK COMES FROM
Here's what matters: the faster cows get to peak milk, and the higher that peak is, the better the rest of the season looks. Those first 48 hours post-calving are when milk fever and subclinical hypocalcaemia rob most cows of their ability to hit that peak.
THE LATEST TRIAL RESULTS
The most recent published trial (November 2024) from Anchor Life Sciences and vets at University College Dublin tested Cow Start Complete on 26 cows from a 280-cow pasture-fed Irish herd producing around 6,600kg per season (21L/cow/day). The herd had Allflex collars and individual daily milk weight recording - proper data, not guesswork.
What the study showed:
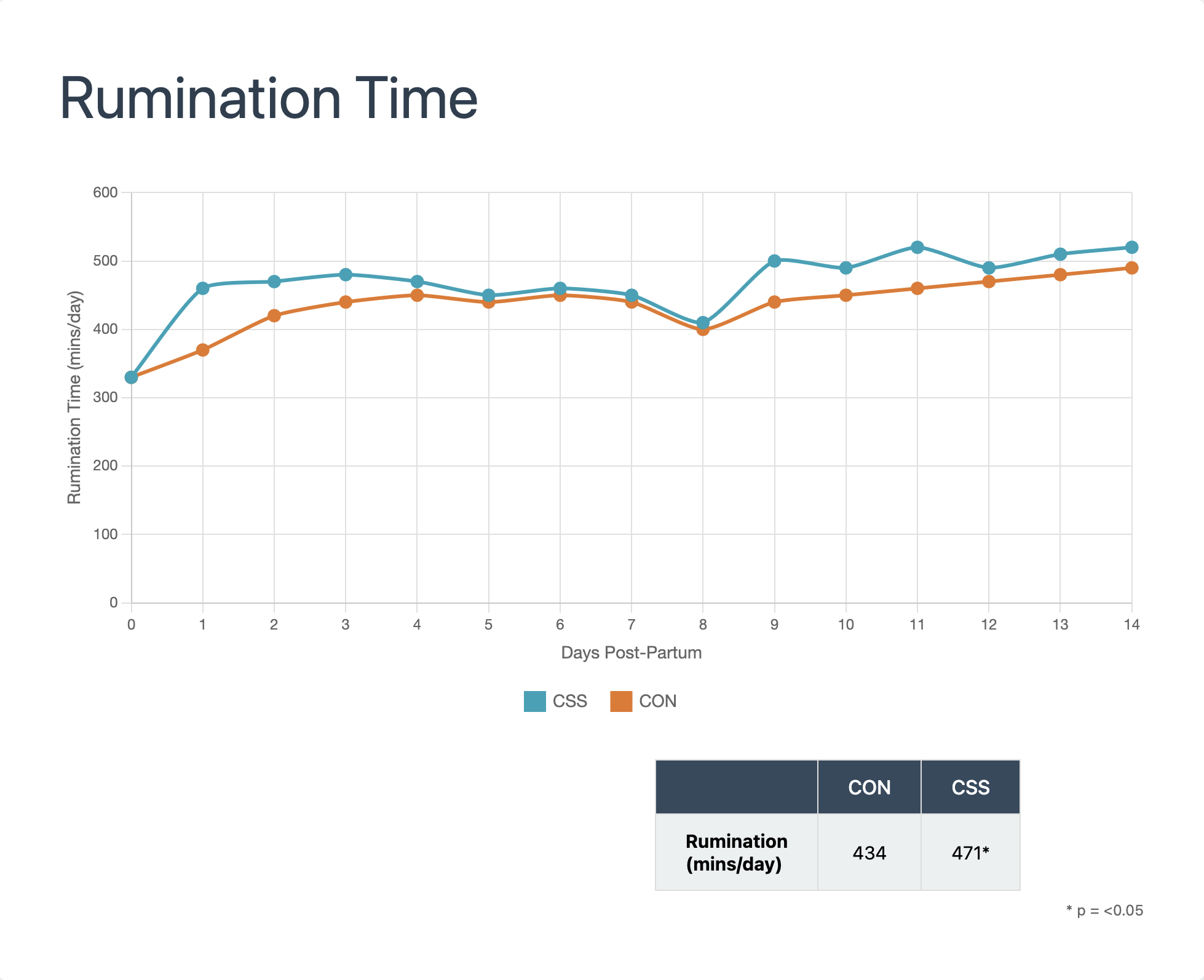
Cow Start kept serum calcium above the subclinical hypocalcaemia threshold for the full 48 hours post-calving
This translated to significantly better rumination
Which delivered +1.8kg/cow/day milk production during the first 12 weeks of lactation (NZ farmers note: the analysis was in kg of whole milk - not solids!)
HOW IT STACKS UP AGAINST ALTERNATIVES
A meta-analysis review of Cow Start research across different production systems shows consistent results:
6,000kg grass-based systems
9,000kg mixed systems
12,000kg intensive indoor production
Across all these systems, Cow Start consistently increases milk production by approximately 4.6% over the full lactation.
The trial results line up with several other studies showing Cow Start consistently outperforms:
Unsupplemented control cows: +1.3kg/day (P<0.05)
Short-acting calcium bolus: +0.8kg/day (P<0.10)
Short-acting calcium bolus AND calcium oral fluid therapy: +1.6kg/day
That's not just statistical noise - that's real milk in the vat.
It's not complicated. Keep calcium status right through those critical first 48 hours, rumination stays up, feed intake stays up, and the cow has the metabolic foundation to actually perform. Short-acting boluses run out of steam halfway through the danger zone. Cow Start Complete covers the whole period when it matters most.
References
1. Lawlor, J. et al. “Can supplementation with the Cow Start Complete Bolus result in elevated blood calcium status in a group of at risk dairy cows during the first 4 days of lactation” Animal & Veterinary Sciences Vol. 12, (6), pp 154-160. 2024
2. Fahey, A., Lawlor. J., Cow Start Research Meta-analysis, 2022
3. J. Lawlor, A. Fahey, E. Neville, A. Stack, and F. Mulligan, “On-farm Safety and Efficacy Trial of Cow Start Calcium Bolus,” Anim. Vet. Sci., vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 121–126, 2019.
4. Lawlor, J., Fahey, A., Neville, E., Stack, A., and Mulligan, F. “Effect of Cow Start Calcium Bolus on Metabolic Status and Milk Production in Early Lactation”, Anim Vet Sci., vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 124-132, 2020.